Key Takeaways
- Where dome cameras are deployed, including toll zones, tunnels, and semi-public spaces
- Strengths (compact size, ONVIF support, etc.) and limitations (restricted FoV, limited zoom, etc.) of dome cameras
- Common use cases of bullet cameras like speed enforcement and multi-lane free-flow tolling
- Critical features of bullet cameras, such as high resolution, zoom, and low-light performance
Every second matters in traffic enforcement. Poor visibility, narrow field of view, and lag in detection can weaken enforcement systems and limit incident response. The camera form factor has a direct role in system performance.
Dome and bullet cameras each bring distinct mechanical, optical, and integration traits. But in traffic and outdoor use, one clearly takes the lead.
In this blog, you’ll learn about both types of cameras before finding out why bullet cameras are increasingly preferred for smart traffic management and outdoor surveillance.
What Are Dome Cameras?
Dome cameras are enclosed surveillance units known for their compact design. The name comes from their dome-shaped outer casing that shields the lens and hardware. They’re mounted on ceilings or poles and are often used in fixed-angle indoor or semi-outdoor deployments.
Their discrete profile makes them suited for security monitoring where deterrence is a secondary concern. In traffic deployments, their use remains limited due to fixed optics and narrower environmental tolerance.
Where Dome Cameras Are Used
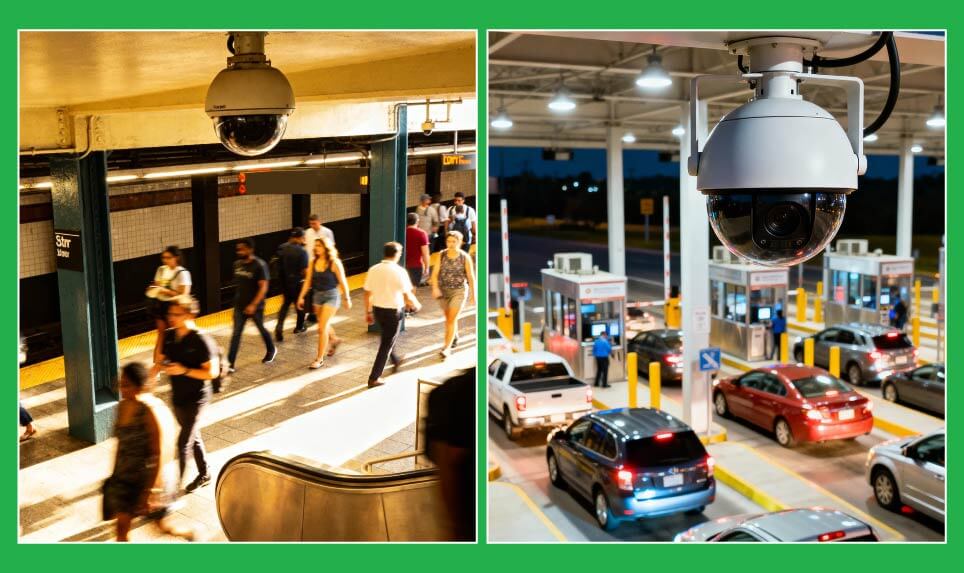 Parking and toll zones
Parking and toll zones
Dome cameras are widely installed in parking areas and toll booths where vehicles move slowly and lighting remains uniform. Their overhead mounting enables continuous observation of entry and exit lanes, ticket kiosks, and payment points. The sealed design maintains clarity under artificial illumination, ensuring consistent imaging across predictable traffic flow.
Tunnels and metro stations
Confined infrastructure, such as tunnels or underground stations, benefits from dome enclosures. The compact structure fits tight ceilings, providing stable coverage for restricted zones and low-clearance areas. Fixed viewing angles simplify calibration in environments where the field of view remains constant.
Pedestrian and semi-public spaces
Deployed in crosswalks, terminals, and sheltered waiting zones, dome cameras help monitor both vehicles and foot movement. The unobtrusive shape prevents visual distraction in crowded areas while ensuring constant visibility for incident review or crowd control.
Strengths of Dome Cameras
Discrete and compact form factor
The enclosed design conceals lens direction, which discourages tampering and maintains a neutral visual profile. It is useful for stations, plazas, and indoor facilities where camera visibility can influence behavior or aesthetics.
Vandal and dust resistance
Dome housings protect sensors from impact, dust, and moisture. They minimize mechanical damage in public settings and sustain performance over extended duty cycles under controlled conditions.
Integration with indoor infrastructure
Mounting options align with interior lighting layouts and low ceilings, making dome cameras ideal for covered checkpoints or compact traffic booths where directional flexibility is less critical.
Stable imaging for short-range monitoring
Fixed optics perform well when the camera operates within a defined radius. It enables clear plate recognition at toll gates, accurate monitoring of vehicle queues, and consistent visibility in low-speed environments. However, dome cameras generally lack the optical precision needed for accurate license plate recognition.
RTSP and ONVIF support
Dome cameras support RTSP streaming and ONVIF protocols for seamless integration with VMS platforms, NVRs, and analytics systems. They ensure stable operation and easy configuration across monitoring environments.
Limitations of Dome Cameras in Traffic Enforcement
Restricted field of view
Dome cameras typically have a wider field of view, which helps in close or semi-enclosed areas. Bullet cameras, however, deliver narrower but longer-range focus, improving detection accuracy in open-road or high-speed vehicle monitoring.
Limited optical zoom
Most dome variants rely on fixed lenses, restricting range for identifying distant objects or capturing detail across wider intersections. This shortfall affects enforcement analytics that depend on long-range clarity.
Infrared reflection at night
Curved glass coverings can reflect IR emissions back into the sensor. During low-light operations, glare and motion blur may occur, degrading plate legibility and object contours under artificial light sources.
Lower outdoor durability
Compared to bullet designs, dome cameras carry lower IP ratings and weaker vibration resistance. Exposure to rain, dust, or extreme heat can lead to gradual image drift or hardware fatigue, reducing suitability for roadside enforcement.
How Are PTZ Dome Cameras Used in City Surveillance?
PTZ dome variants extend capability through motorized control, allowing operators to pivot, tilt, and zoom for wide-area visibility. They fit large-scale grids that require dynamic coverage rather than fixed enforcement points.
Benefits
- Adjustable orientation supports live tracking of vehicles and pedestrians across intersections
- Programmable patrol routes automate the scanning of city squares or parking clusters
Trade-offs
- Moving assemblies increase wear, calibration effort, and long-term maintenance
- Image stability declines under strong vibration or weather exposure compared to fixed bullet units
What Are Bullet Cameras?
Bullet cameras are built for directional focus, weather exposure, and longer distances. These units extend outward on mounting arms and typically support high-resolution sensors with optical zoom. The design enables faster component cooling, more stable alignment under vibration, and better low-light performance due to lens positioning.
In traffic enforcement, bullet cameras address a specific set of challenges. These include poor nighttime visibility, fixed zoom limitations, bandwidth-heavy backhaul, and long deployment cycles. They are field-proven in roadside deployments where reliability, clarity, and response speed determine system value.
Why Bullet Cameras Are Preferred Over Dome Cameras
High-resolution imaging
Traffic surveillance requires granular data at high speeds. Bullet cameras support 5MP and 8MP sensors to deliver sharp imaging across multiple lanes. The level of clarity enables automated plate detection, color capture, and vehicle type classification at a distance.
Flexible zoom
Zoom range can determine incident coverage. Bullet units offer 4x and 18x optical zoom variants to adjust framing for near-lane and far-lane traffic. Operators can tune view parameters based on road width, intersection shape, or enforcement zone.
Night vision with strobe IR
Standard IR systems may miss fine details in low light. Bullet cameras pair smart IR with strobe flash to handle fog, glare, or low ambient light. License plates, pedestrian movements, and obstruction events stay visible under challenging conditions.
Edge AI processing
Onboard NPUs handle analytics without routing video to remote servers. It reduces delay and bandwidth load. Using bullet cameras, violation events are detected and tagged on-device with timecodes, location, and object class metadata.
Rugged and weatherproof
Bullet cameras are sealed with IP66 or IP67 protection for roadside use. The units are tested against shock and vibration to prevent internal displacement. They operate continuously through rain, heat, wind, or vehicle-induced tremors.
Low power consumption
Designed for deployment in remote zones, bullet cameras run on low power. Their components are selected for continuous uptime under limited energy budgets, making them suitable for solar-powered enforcement cabinets or standalone poles.
Smart integration
Bullet cameras connect directly with radar, LiDAR, and in-ground trigger sensors through standard I/O. So, it’s possible to link hardware inputs with optical capture workflows. Events like line crossing, speed trigger, or red-light violation can be recorded with synchronized footage.
RTSP and ONVIF support
Bullet cameras support RTSP streaming and ONVIF protocols for direct integration with VMS platforms, NVRs, and analytics tools. They maintain stable connections and consistent data flow across large outdoor deployments.
Popular Use Cases of Bullet Cameras
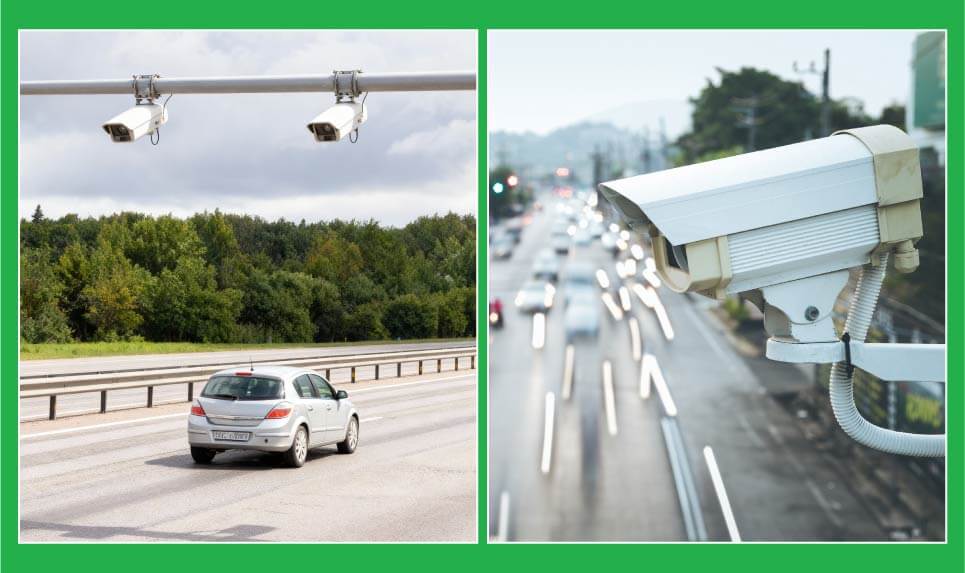 Speed enforcement
Speed enforcement
Bullet cameras monitor target zones for velocity thresholds using object tracking and time-distance calculations. Their optical zoom provides frame-level clarity over extended stretches, while onboard processors calculate speed instantly. It supports both radar-assisted and radar-independent deployments.
Red light detection
Mounted at junctions, bullet cameras capture license plates and vehicle movement across signal phases. High-resolution sensors and synchronized flash IR maintain plate visibility even during motion blur or reflective interference.
MLFF (Multi-Lane Free Flow) Tolling
Bullet cameras deliver sharp, consistent imaging for MLFF tolling systems. Their extended range and adjustable lenses enable clear license plate recognition across multiple lanes, even when vehicles move at higher speeds.
e-con Systems Offers High-Performance Bullet Cameras
Since 2003, e-con Systems has been designing, developing, and manufacturing OEM cameras.
We offer high-performance bullet cameras that help overcome key smart traffic and outdoor surveillance challenges, from unreliable nighttime visibility and limited zoom flexibility to integration delays and high-power consumption.
These cameras combine high-resolution sensors, optical zoom, strobe-supported IR night vision, and onboard AI — all inside a rugged, low-power design. They offer uninterrupted performance in harsh outdoor environments while supporting faster deployment with industry-standard protocols.
Explore our Camera Selector and discover our full portfolio.
Know more about our smart traffic cameras
If you need an expert to help you integrate the ideal bullet camera into your embedded vision application, please write to camerasolutions@e-consystems.com.

Dilip Kumar is a computer vision solutions architect having more than 8 years of experience in camera solutions development & edge computing. He has spearheaded research & development of computer vision & AI products for the currently nascent edge AI industry. He has been at the forefront of building multiple vision based products using embedded SoCs for industrial use cases such as Autonomous Mobile Robots, AI based video analytics systems, Drone based inspection & surveillance systems.